Basically, compared to legacy analog systems, digital radio networks give:
- More capacity from the same number of frequencies; that is, they provide superior Spectral Efficiency1. This is a result of the modulation methods used, and the fact that, in many cases more than one ‘conversation’ can be accommodated within a single radio channel.
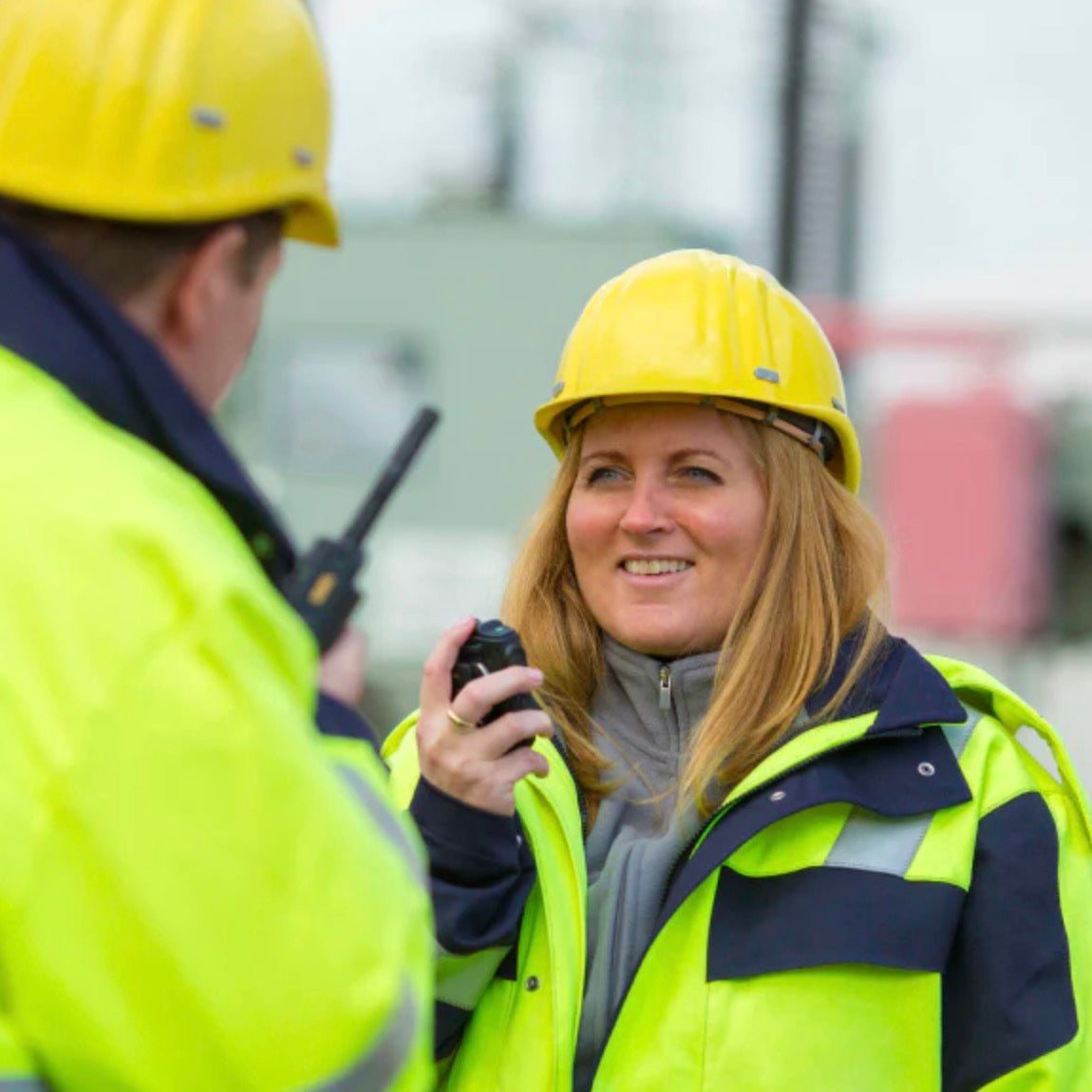
- Consistent voice clarity at low received signal levels near the edge of coverage. The general consensus is that digital radios provide better audio quality than analog ones. With analog FM radios, the audio quality steadily declines as the received signal strength gets weaker. Digital radios however, will have a consistent audio quality throughout the full service area. The edges of the coverage area in a digital radio system are similar to those experienced with cellular telephones.
- Data is defined in the standard. This means data implementations are no longer proprietary, there are a wide variety of data mechanisms and interoperability can extend into the data domain. With the accepted increase of efficiency by using data communications over voice, this will further increase the usability and effectiveness of digital radio systems.
- Secure transmissions in digital technologies, data and voice can be secured using encryption without impacting voice quality using industry standard encryption techniques.