World War II was a turning point in both global history and technological innovation, driving advancements that would shape the modern world. Among these innovations, the development of two-way radios played a crucial role in military communication, and their legacy continues to impact civilian and commercial applications today. This article explores how World War II influenced the development of two-way radios in the United States, focusing on the technological, industrial, and tactical changes that emerged during the war.
1. Technological Advancements Driven by Warfare
The intense demands of World War II accelerated innovations in radio technology. Before the war, two-way radios were bulky and limited in range. However, the exigencies of modern warfare pushed for more portable, reliable, and efficient communication systems.
-
Frequency Modulation (FM) Technology: FM technology significantly improved the quality and reliability of radio communications by reducing interference and providing clearer audio transmission. This made radios more practical for use in combat zones.
-
Miniaturization: To make radios more portable for soldiers, advances in circuit design allowed for the miniaturization of components. This made two-way radios more compact and lightweight, ideal for military operations on the move.
-
Improved Antennas and Power Sources: Enhancements in antenna design and battery technology extended the range and operational life of radios, ensuring communication remained uninterrupted in challenging environments.
These wartime innovations set the stage for modern two-way radio technology, providing faster and more secure communication.
2. Mass Production and Industrial Mobilization
The scale of World War II required immense levels of production, and two-way radios were among the most essential tools for military operations. This led to significant changes in manufacturing processes.
-
Rapid Scaling of Manufacturing: U.S. companies like Motorola ramped up production to meet the military’s demand for radios. The ability to mass-produce two-way radios meant that the U.S. military could equip soldiers with reliable communication devices on a large scale.
-
Standardization: To ensure seamless interoperability across various units and operations, standardized specifications for two-way radios were established. This enabled more efficient communication during complex military operations.
-
Supply Chain Optimization: The need for consistent radio production during the war led to the development of robust supply chains. This infrastructure was crucial not only for wartime efforts but also for post-war civilian applications.
3. Tactical Applications on the Battlefield
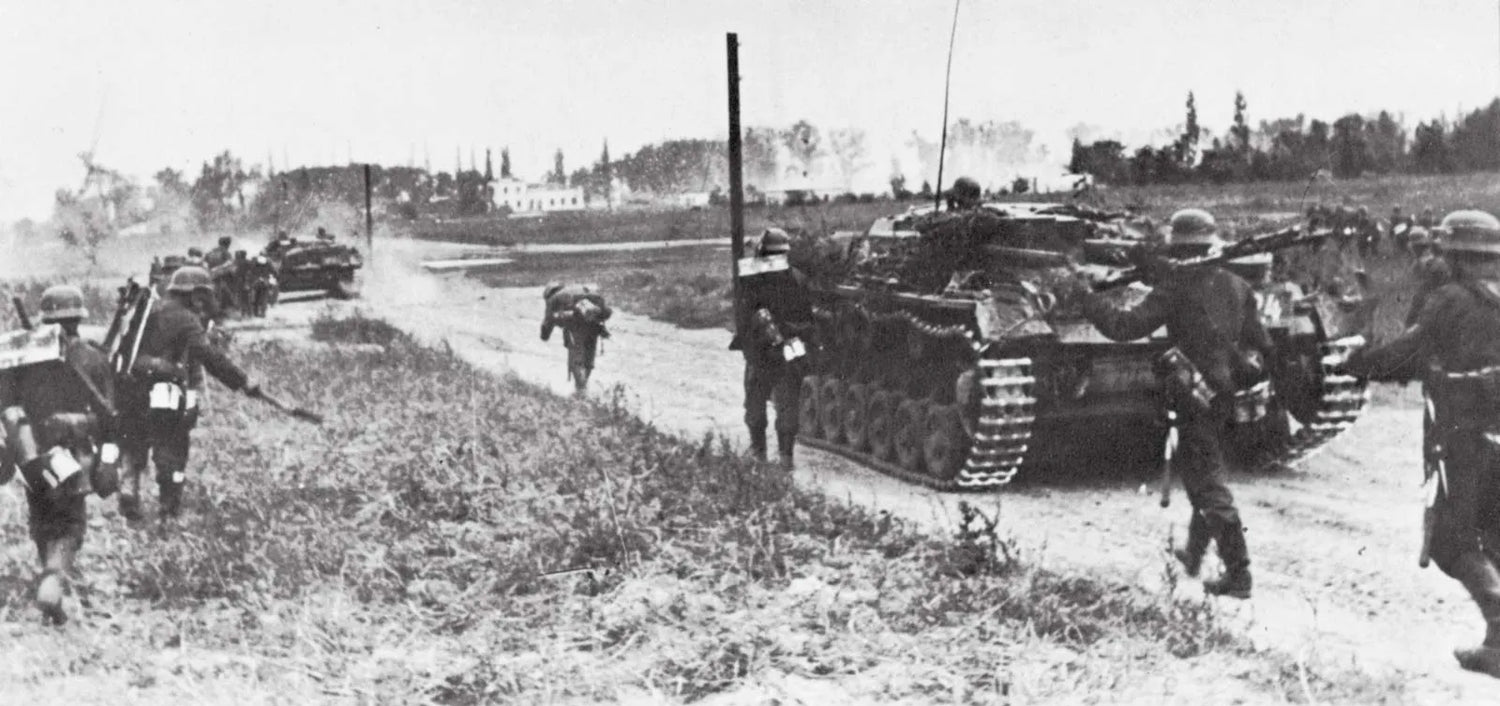
Two-way radios transformed military tactics by enabling real-time communication between units, a critical factor in the success of military operations.
-
Command and Control: Radios allowed commanders to issue orders and receive updates from the front lines instantly, improving the speed and accuracy of decision-making.
-
Coordination of Multi-Troop Operations: Radios facilitated the synchronization of infantry, air, and armor units, enabling more effective combined arms operations.
-
Intelligence Gathering: The ability to communicate rapidly allowed intelligence to be disseminated in real-time, helping troops adapt quickly and respond to emerging threats.
The tactical advantages provided by two-way radios underscored their importance in modern warfare and highlighted their essential role in military strategy.
4. Post-War Civilian Adoption
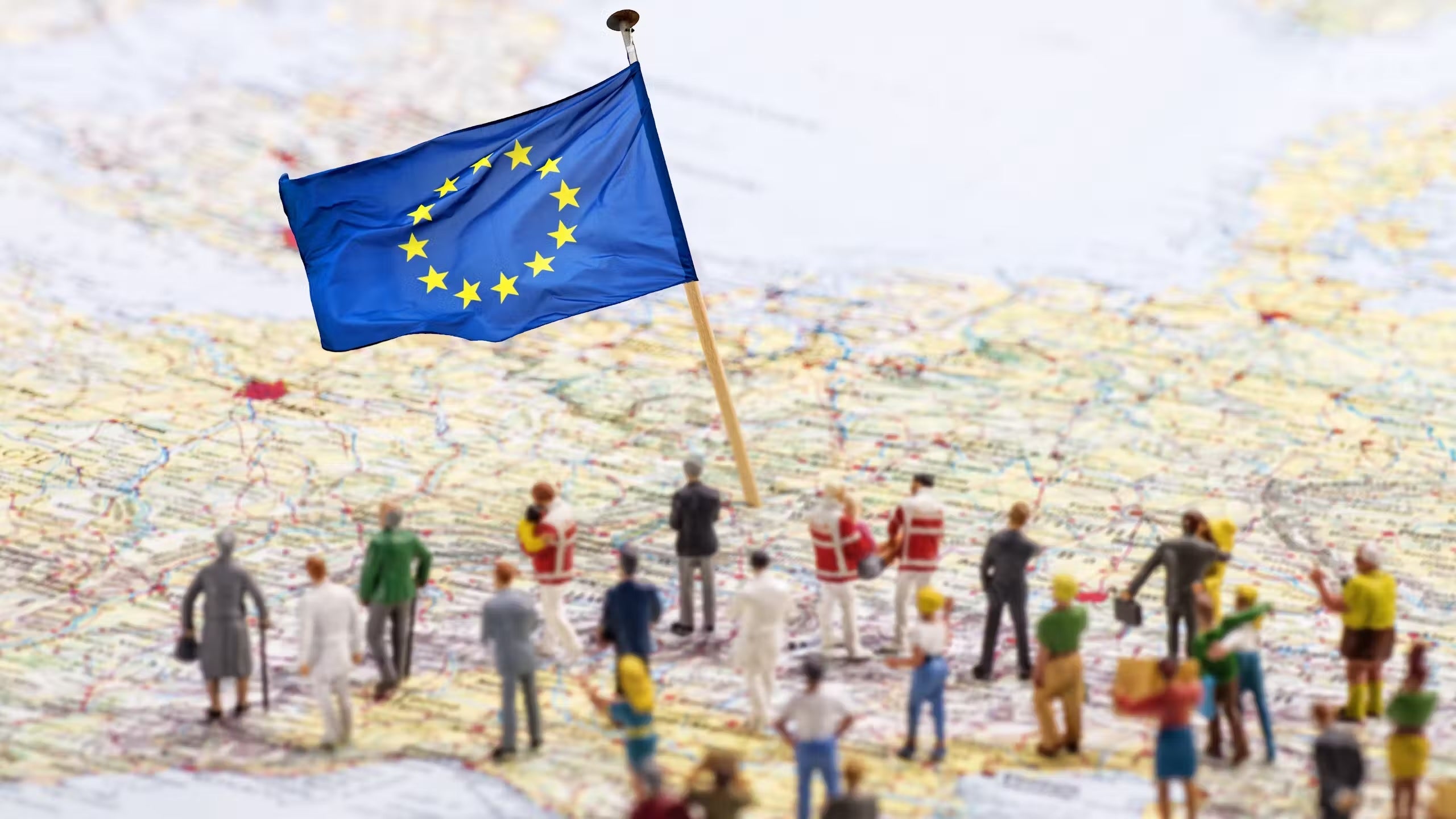
After World War II, two-way radios began to transition from military use to civilian applications, expanding their reach and utility.
-
Technological Spin-offs: Innovations developed during the war, such as FM modulation and miniaturization, found their way into civilian markets. These technological spin-offs democratized access to radio communication, making two-way radios accessible for businesses and personal use.
-
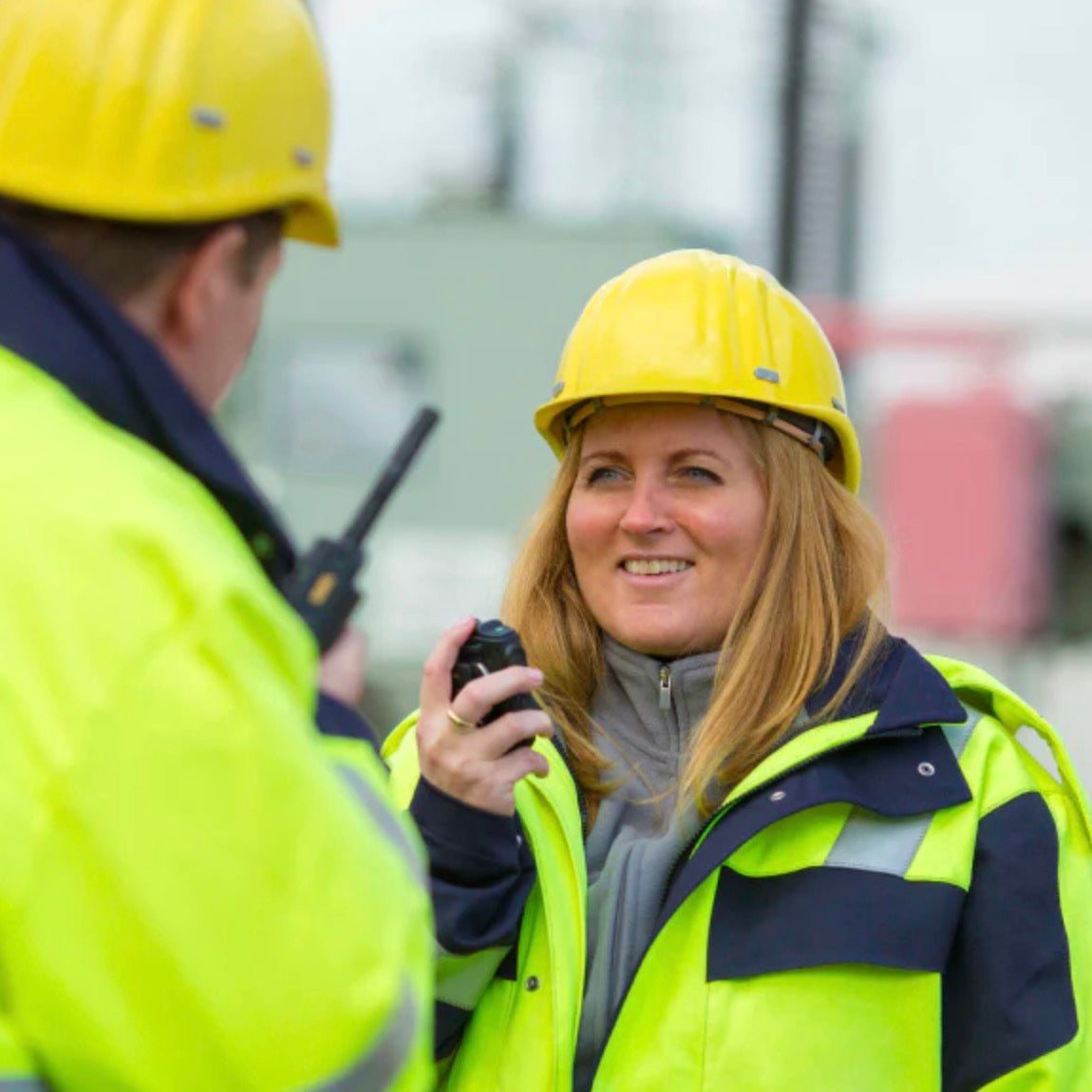
Growing Market Demand: The post-war economic boom created a thriving market for consumer electronics, and two-way radios quickly became popular for industries such as transportation, construction, and emergency services.
-
Regulatory Frameworks: The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) introduced regulations to manage civilian radio frequencies, ensuring the safe and organized use of the airwaves.
The post-war era saw two-way radios evolve from military tools into versatile communication devices with widespread applications.
5. Modern Developments Inspired by WWII Legacy
The technological advancements and lessons learned during World War II continue to influence the development of modern two-way radios.
-
Digital Communication: Building on wartime innovations, digital two-way radios now offer clearer audio, better security, and the ability to transmit data alongside voice communication.
-
Integration with Other Systems: Contemporary radios often incorporate GPS, data transmission, and other advanced technologies, expanding their functionality across various industries.
-
Public Safety Applications: Two-way radios remain a critical tool for emergency responders, reflecting their enduring importance in ensuring public safety and effective communication.
Conclusion
World War II was a pivotal moment for the development of two-way radios in the United States, driving technological advancements, mass production capabilities, and tactical innovations that would lay the foundation for their widespread use in civilian sectors. These wartime innovations not only met the military's immediate communication needs but also set the stage for the adoption of two-way radios in industries such as public safety, logistics, and emergency services.
Today, the legacy of World War II continues to shape the evolution of two-way radios, ensuring their relevance in both military and civilian applications. As technology advances, two-way radios will remain essential tools for communication, reflecting the ingenuity and resilience that emerged from one of history's most challenging periods.









































Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.