When it comes to radio communication, UHF (Ultra High Frequency) and VHF (Very High Frequency) are the two most commonly used frequency bands. But how do they differ, and which one is right for your needs? Understanding the basics of UHF and VHF can help you choose the best option for your specific application.
1. What Are UHF and VHF?
• VHF (30 MHz – 300 MHz): VHF operates on lower frequencies and is commonly used for long-distance communication with fewer obstacles, such as in open fields, marine communication, or aviation.
• UHF (300 MHz – 3 GHz): UHF operates on higher frequencies and is better suited for densely populated areas or indoor environments where signals need to penetrate walls and obstructions.
2. Signal Range
• VHF Advantages: VHF waves are longer and can travel further in open spaces, making them ideal for outdoor applications. However, they struggle in urban areas with buildings and obstructions.
• UHF Advantages: UHF waves are shorter and can penetrate through obstacles like walls, making them better for indoor use or in crowded areas like cities.
3. Antenna Size
• VHF: Requires longer antennas due to its lower frequency. This can be a drawback for handheld devices but works well for fixed installations.
• UHF: Supports shorter antennas, making it more convenient for portable radios and compact devices.
4. Applications
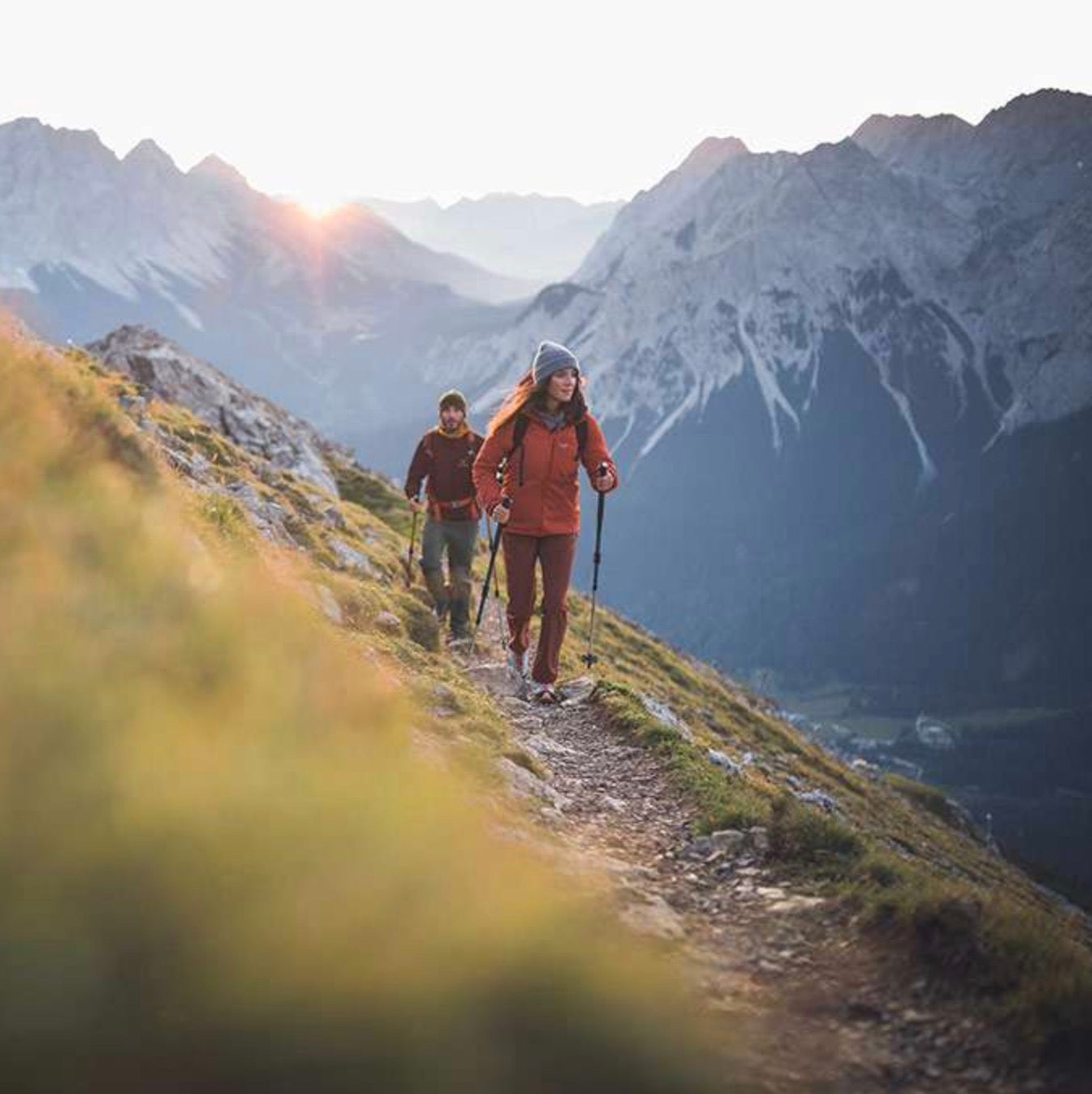
• VHF: Best for:
• Rural and outdoor communication
• Aviation and maritime communication
• Amateur radio operators (HAM)
• UHF: Best for:
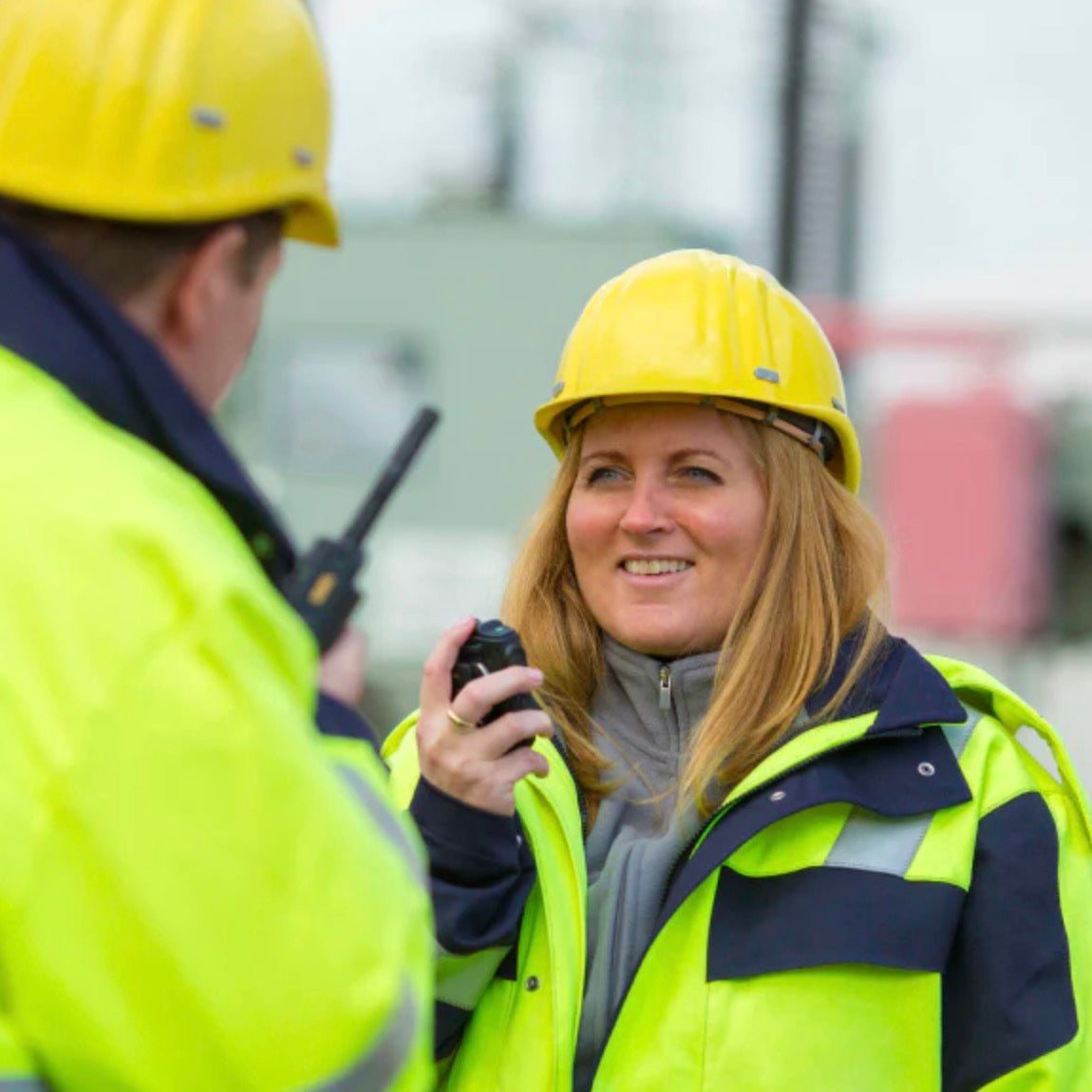
• Urban and indoor environments
• Security teams in buildings or malls
• Professional settings like event coordination
5. Cost Considerations
• VHF devices tend to be slightly cheaper due to simpler technology.
• UHF devices, while pricier, offer better versatility for modern urban environments.
6. Choosing the Right Frequency
When deciding between UHF and VHF, consider these factors:
• Environment: Will you be indoors or outdoors?
• Distance: Do you need long-range communication?
• Obstacles: Are there walls, buildings, or other obstructions?
7. Emerging Technologies
With advancements in digital communication, both UHF and VHF are now being integrated into dual-band radios, allowing users to switch frequencies as needed. This hybrid approach is becoming a game-changer for industries requiring flexible communication options.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice
Both UHF and VHF have unique strengths and applications. By understanding your communication needs, you can choose the right frequency for your personal or professional use. Whether it’s for a farming operation, an urban security team, or outdoor exploration, UHF and VHF frequencies play an essential role in reliable communication.










































Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.