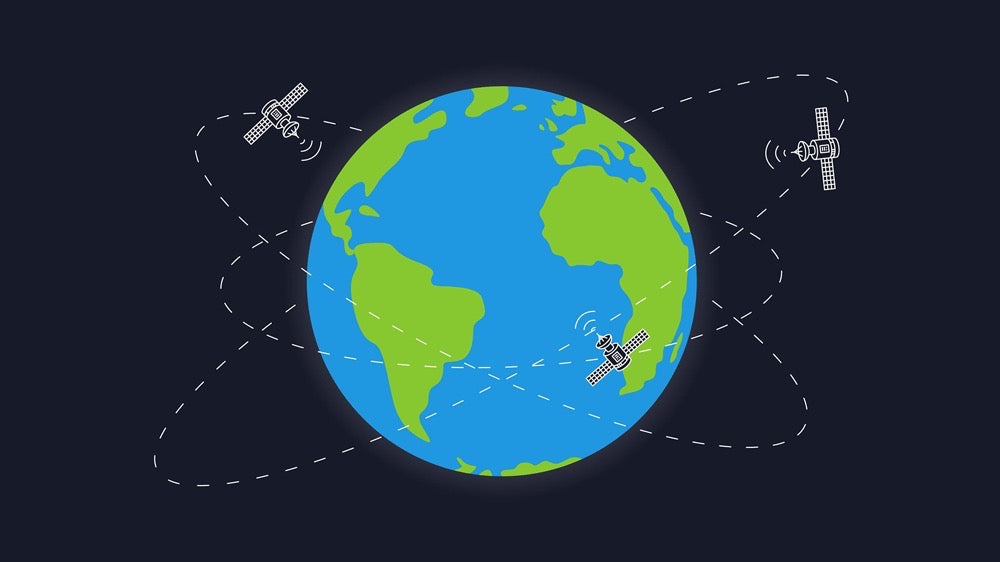
Global Positioning System (GPS) technology has revolutionized the way we navigate our world. This sophisticated system, based on a network of orbiting satellites, provides accurate location and time information to GPS receivers anywhere on Earth, as long as there is an unobstructed line of sight to four or more GPS satellites.
The genesis of GPS can be traced back to the desire for a precise navigational system. Its development was fueled by the need for accurate, real-time location information in various applications, from military operations to civilian usage in navigation, mapping, and surveying.
GPS operates through a constellation of satellites that transmit signals to receivers on the ground. These signals, when processed, provide information about the receiver's location, speed, and direction. This process, known as trilateration, involves measuring the distance between the receiver and several satellites to pinpoint the receiver's exact position on Earth.
The impact of GPS technology on modern life is profound. It has transformed navigation, enabling precise point-to-point navigation for vehicles, aircraft, and ships. Beyond navigation, GPS has applications in a multitude of fields including agriculture, for precision farming; geology, for earthquake research and monitoring; and even in finance, for time-stamping transactions in the global financial system.
As GPS continues to evolve, its integration with other technologies like smartphones and the internet of things (IoT) has led to innovative applications that influence our daily lives. From locating emergency callers to monitoring the movements of wildlife and assets, GPS has become a foundational technology in our interconnected world.
In conclusion, GPS is more than just a tool for finding our way; it's a critical infrastructure component that supports many aspects of modern society. Its precise time and location capabilities have made it an indispensable technology for global operations and personal convenience.